AWS Database Migration Service
What is AWS Database Migration Service?#
At a basic level, AWS DMS is a server (Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) in the AWS Cloud that runs replication software. You create a source and target connection to tell AWS DMS where to extract data from and where to load it Next, you schedule a task that runs on this server to move your data. YOu can create the target tables and primary keys etc yourself or use AWS Schema Conversion Tool to do it for you.
Migrate relational databases, data warehouses, NoSQL databases, and other types of data stores.
- Discover data source with DMS Fleet Advisor - gets on premise database and analytics servers and builds an inventory
- DMS Schema Conversion - to migration to a different database engine
- AWS DMS to migrate your data: one-time migrations or replicate ongoing changes to keep sources and targets in sync

High Level Overview#
After discovery and the creating of schemas on targets / conversions.
- Create a replication server.
- Create source and target endpoints that have connection information about your data stores.
- Create one or more migration tasks to migrate data between the source and target data stores.
A task has 3 major phases:
- Migration of existing data (Full load)
- The application of cached changes
- Ongoing replication (Change Data Capture)
While the full load is in progress, any changes made to the tables being loaded are cached on the replication server
When the full load for a given table is complete, AWS DMS immediately begins to apply the cached changes for that table
You can use AWS DMS to take a minimalist approach and create only those objects required to efficiently migrate the data. Using this approach, AWS DMS creates tables, primary keys, and in some cases unique indexes, but it won’t create any other objects that are not required to efficiently migrate the data from the source.
Components#
Replication InStance#
A single replication instance can host multiple replication tasks:
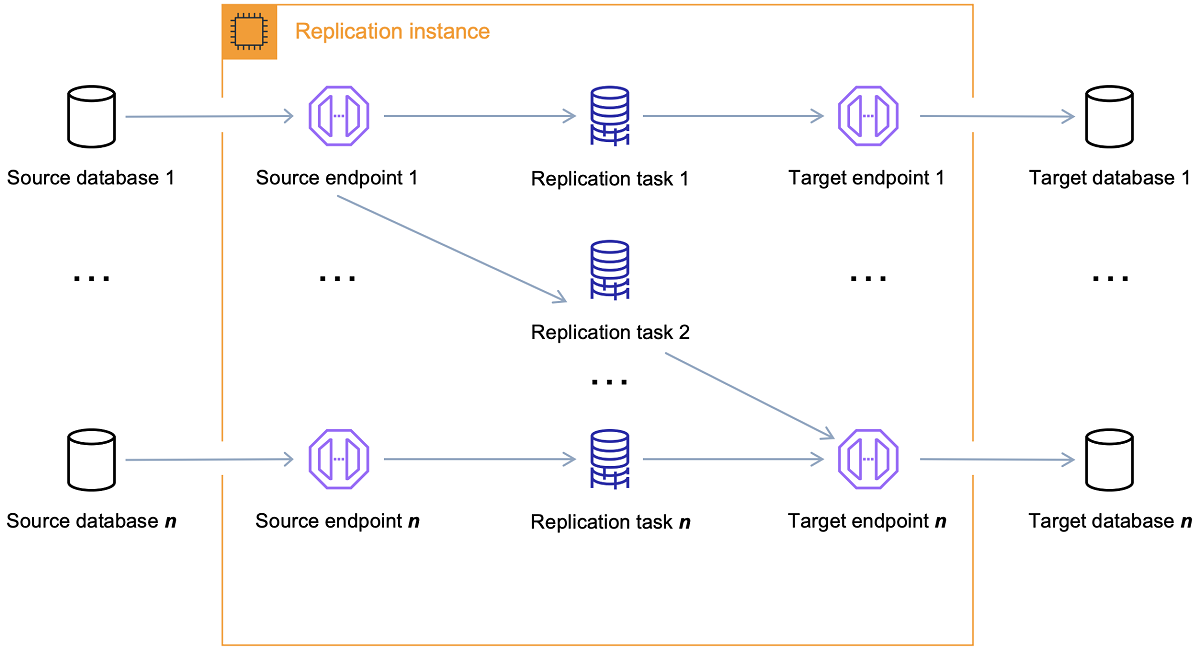
Endpoint#
AWS DMS uses an endpoint to access your source or target data store.
- Endpoint type – Source or target.
- Engine type – Type of database engine, such as Oracle or PostgreSQL.
- Server name – Server name or IP address that AWS DMS can reach.
- Port – Port number used for database server connections.
- Encryption – Secure Socket Layer (SSL) mode, if SSL is used to encrypt the connection.
- Credentials – User name and password for an account with the required access rights.
Replication tasks#
You use an AWS DMS replication task to move a set of data from the source endpoint to the target endpoint
Task settings are specified on create:
- Replication instance – the instance to host and run the task
- Source endpoint
- Target endpoint
- Migration type options
- Full load (Migrate existing data) – If you can afford an outage long enough to copy your existing data, this option is a good one to choose. This option simply migrates the data from your source database to your target database, creating tables when necessary.
- Full load + CDC (Migrate existing data and replicate ongoing changes) – This option performs a full data load while capturing changes on the source. After the full load is complete, captured changes are applied to the target. Eventually, the application of changes reaches a steady state. At this point, you can shut down your applications, let the remaining changes flow through to the target, and then restart your applications pointing at the target.
- CDC only (Replicate data changes only) – In some situations, it might be more efficient to copy existing data using a method other than AWS DMS. For example, in a homogeneous migration, using native export and import tools might be more efficient at loading bulk data. In this situation, you can use AWS DMS to replicate changes starting when you start your bulk load to bring and keep your source and target databases in sync.
- Target table preparation mode options
- Do nothing – AWS DMS assumes that the target tables are precreated on the target.
- Drop tables on target – AWS DMS drops and recreates the target tables.
- Truncate – If you created tables on the target, AWS DMS truncates them before the migration starts. If no tables exist and you select this option, AWS DMS creates any missing tables.
- LOB mode options:
- Don’t include LOB columns – LOB columns are excluded from the migration.
- Full LOB mode – Migrate complete LOBs regardless of size. AWS DMS migrates LOBs piecewise in chunks controlled by the Max LOB Size parameter. This mode is slower than using limited LOB mode.
- Limited LOB mode – Truncate LOBs to the value specified by the Max LOB Size parameter. This mode is faster than using full LOB mode.
- Table mappings – indicates the tables to migrate and how they are migrated.
- Data transformations
- Changing schema, table, and column names.
- Changing tablespace names (for Oracle target endpoints).
- Defining primary keys and unique indexes on the target.
- Data validation
- Amazon CloudWatch logging
Ongoing Replication Issues#
In the CDC process, the replication task is designed to stream changes from the source to the target, using in-memory buffers to hold data in-transit. If the in-memory buffers become exhausted for any reason, the replication task will spill pending changes to the Change Cache on disk. This could occur, for example, if AWS DMS is capturing changes from the source faster than they can be applied on the target. In this case, you will see the task’s target latency exceed the task’s source latency.
You can check this by navigating to your task on the AWS DMS console, and opening the Task Monitoring tab. The CDCLatencyTarget and CDCLatencySource graphs are shown at the bottom of the page.
Sources#
On premise:
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Postgres
- MongoDB
- IBM DB2
Third Party:
- Azure and Google Cloud MySQL and Postgres
Amazon RDS instance:
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL
- MySQL
- Postgres
Targets#
On premise:
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Postgres
- Redis
- MariaDB
Amazon RDS instance:
- Amazon Aurora MySQL-Compatible Edition
- Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition
- Amazon Aurora Serverless v2
- Amazon Redshift
- Amazon Redshift Serverless
- Amazon S3
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon OpenSearch Service
- Amazon ElastiCache for Redis
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
- Amazon DocumentDB (with MongoDB compatibility)
- Amazon Neptune
- Apache Kafka – Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) and self-managed Apache Kafka
- Babelfish (version 3.2.0 and higher) for Aurora PostgreSQL (versions 15.3/14.8 and higher)
Resource Names#
A resource can be named:
arn:aws:dms:region:account number:resourcetype:resourcename
examples:
- Replication instance:
arn:aws:dms:us-east-1:123456789012:rep:QLXQZ64MH7CXF4QCQMGRVYVXAI - Endpoint:
arn:aws:dms:us-east-1:123456789012:endpoint:D3HMZ2IGUCGFF3NTAXUXGF6S5A - Replication task:
arn:aws:dms:us-east-1:123456789012:task:2PVREMWNPGYJCVU2IBPTOYTIV4 - Subnet group:
arn:aws:dms:us-east-1:123456789012:subgrp:test-tag-grp
Getting Started#
- Set up your AWS account
- Create your sample databases and an Amazon EC2 client to populate your source database and test replication. Also, create a virtual private cloud (VPC) based on the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) service to contain your tutorial resources.
- Populate your source database using a sample database creation script.
- Use DMS Schema Conversion or the AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) to convert the schema from the source database to the target database.
- Create a replication instance to perform all the processes for the migration.
- Specify source and target database endpoints.
- Create a task to define what tables and replication processes you want to use, and start replication.
Verify that replication is working by running queries on the target database.
Basic:
Ensure source and target exists. Eg. Postgres database source and kafka topic destination.
- Step 1: Create a replication instance - size and networking of EC2 instance
- Step 2: Specify source and target endpoints
- Create the endpoints and test there is connectivity
- Step 3: Create a task and migrate data